CI/CD pipelines can be simple or complex – what makes them efficient are rules that define when and how they run. By using rules, you create smarter CI/CD pipelines, which increase teams' productivity and allow organizations to iterate faster. In this tutorial, you will learn about the different types of CI/CD pipelines and rules and their use cases.
What is a pipeline?
A pipeline is a top-level component of continuous integration and continuous delivery/continuous deployment, and it comprises jobs, which are lists of tasks to be executed. Jobs are organized in stages, which define when the jobs run.
A pipeline can be a basic one in which jobs run concurrently in each stage. Pipelines can also be complex, like parent-child pipelines, merge trains, multi-project pipelines, or the more advanced Directed Acyclic Graph pipelines (DAG).
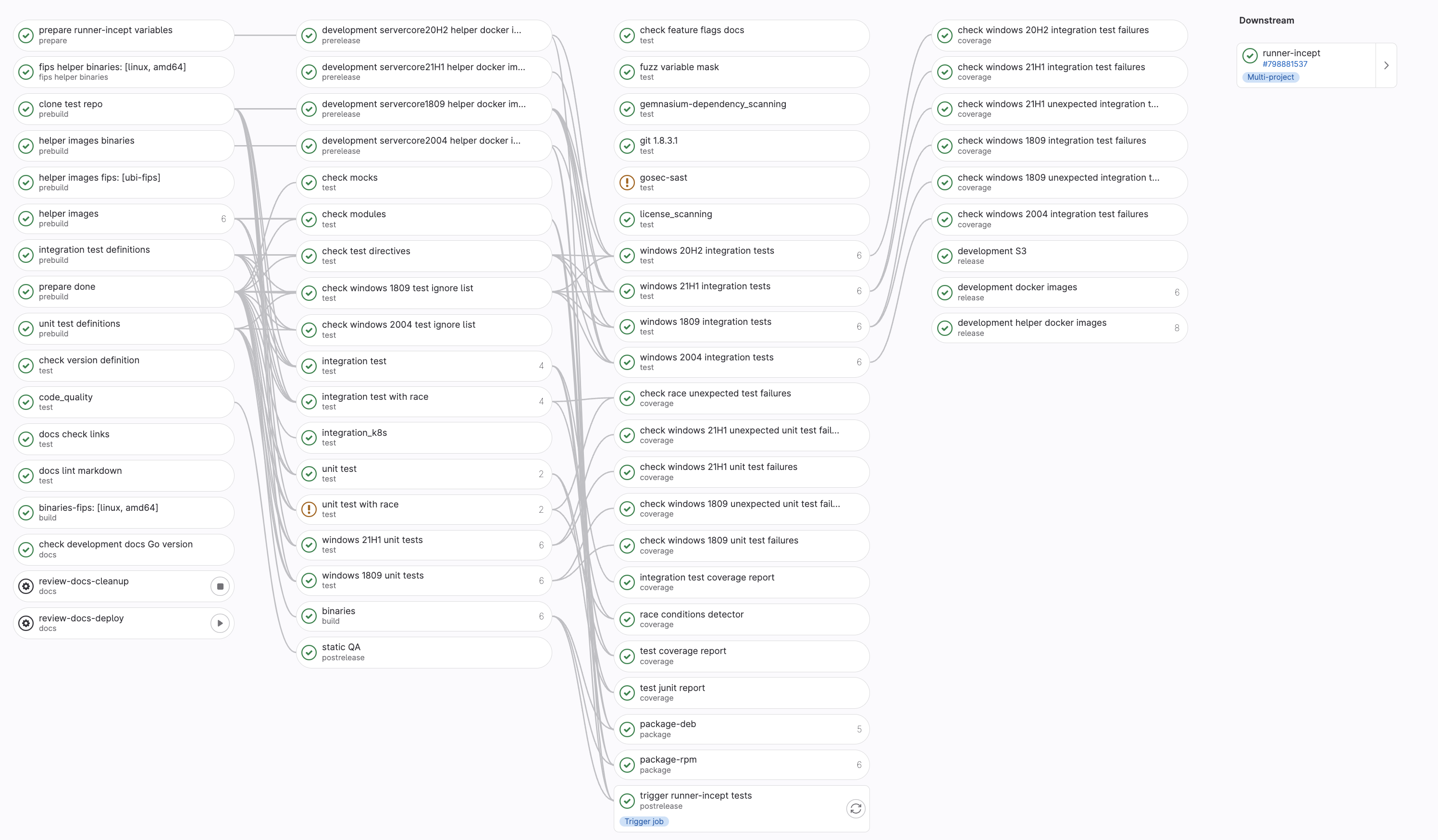
A gitlab-runner pipeline showing job dependencies.
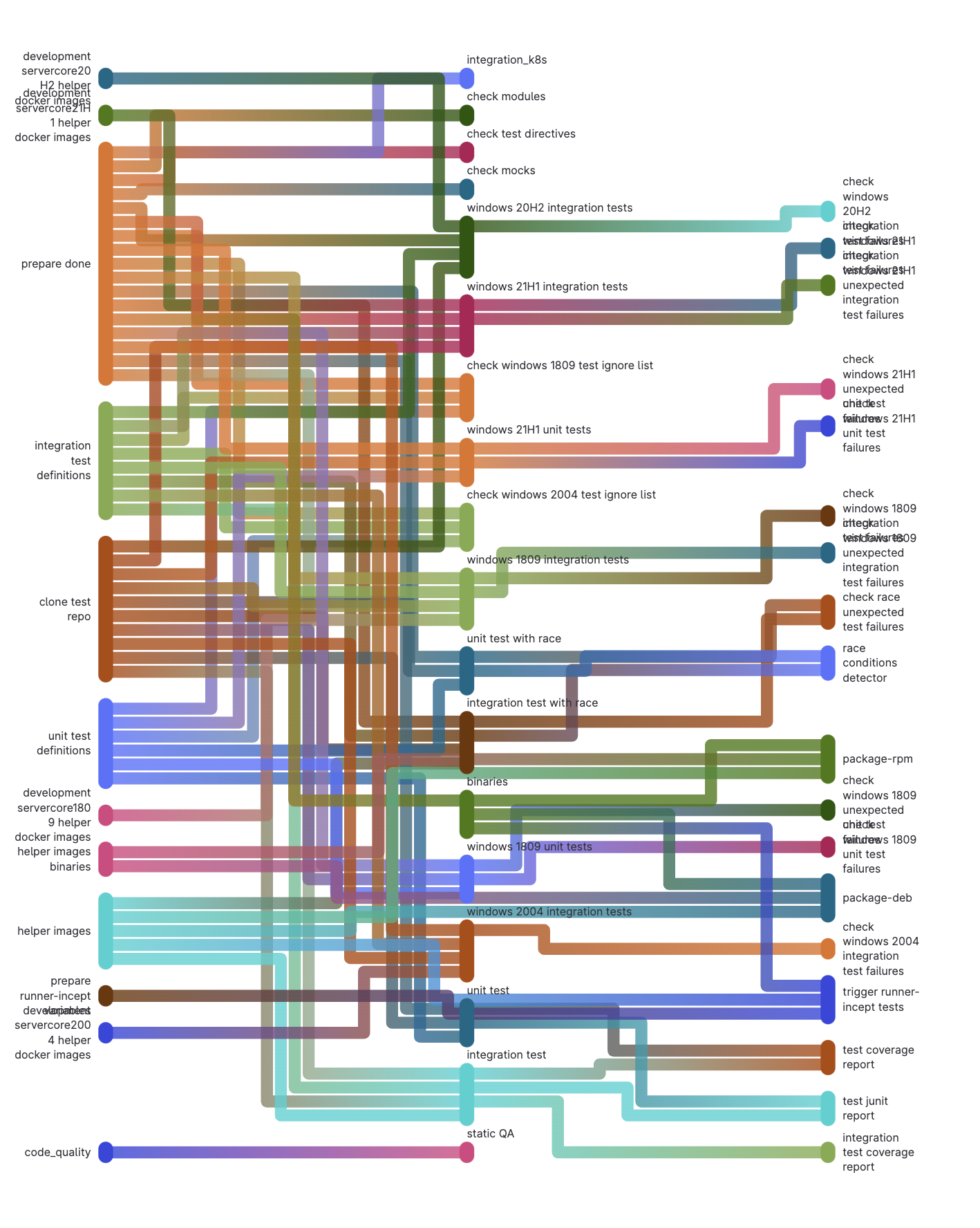
Directed Acyclic Graph pipeline
Use cases determine how complicated a pipeline can get. A use case might require testing an application and packaging it into a container; the pipeline can even further deploy the container to an orchestrator like Kubernetes or a container registry. Another use case might involve building applications that target different platforms with varying dependencies, which is where DAG pipelines shine.
What are CI/CD rules?
CI/CD rules are the key to managing the flow of jobs in a pipeline. One of the powerful features of GitLab CI/CD is the ability to control when a CI/CD job runs, which can depend on context, changes made, workflow rules, values of CI/CD variables, or custom conditions. Aside from using rules, you can also control the flow of CI/CD pipelines using:
needs: establishes relationships between jobs and used in DAG pipelinesonly: defines when a job should runexcept: defines when a job should not runworkflow: controls when pipelines are created
only and except should not be used with rules as this can lead to unexpected behavior. It is recommended to use rules, learn more in the following sections.
What is the rules feature?
rules determine when and if a job runs in a pipeline. If you have multiple rules defined, they are all evaluated in order until a matching rule is found and the job is executed according to the specified configuration.
Rules can be defined using the keywords: if, changes, exists, allow_failure, variables, when and needs.
rules:if
The if keyword evaluates if a job should be added to a pipeline. The evaluation is done based on the values of CI/CD variables defined in the scope of the job or pipeline and predefined CI/CD variables.
job:
script:
- echo $(date)
rules:
- if: $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_SOURCE_BRANCH_NAME == $CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH
In the CI/CD script above, the job prints the current date and time with the echo command. The job is only executed if the source branch of a merge request (CI_MERGE_REQUEST_SOURCE_BRANCH_NAME) is the same as the project's default branch (CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH) in a merge request pipeline. You can use the == and != operators for comparison, while =~ and !~ allow you to compare a variable to a regular expression. You can combine multiple expressions using the && (AND), || (OR) operators, and parentheses for grouping expressions.
rules:changes
With the changes keyword, you can watch for changes to certain files or folders for a job to execute. GitLab uses the output of [Git diffstat](https://git-scm.com/docs/git-diff#Documentation/git-diff.txt



