Modern software development often takes advantage of code reuse. Instead of reinventing the wheel, developers can use a library that focuses on a particular
function for use in an application. However, there is one caveat: These
dependencies may be susceptible to security vulnerabilities, which may render
your whole application – and possibly your software supply chain – as vulnerable.
That is why DevOps teams must be able to generate a software bill of materials, or SBOM. GitLab has partnered with Rezilion to make this task easier.
The need for SBOMs
In 2020, the Solar Winds software supply chain attack happened. Hackers used an easy-to-guess password to inject malicious
code into a software update and many users of the affected Solar Winds product
Orion, including government agencies, had their data compromised.
This breach, along with other high-profile attacks, led Pres. Biden's administration to require software vendors to deliver a software bill of materials (SBOM) with any software offer they make to federal agencies.
Secure your software and manage vulnerabilities
To get started with software supply chain security, you need to not only implement security scanning, but
also have a process in place to manage and effectively triage these vulnerabilities.
Below, you can see the typical software development lifecycle. It shows that security scans are run on a feature branch. A developer can view the presented vulnerabilities and continue to commit to the feature branch which re-runs the scans.
Once the vulnerabilities have been remediated the feature branch can be merged. If vulnerabilities are still present, approval by the security team can be required, and you can continue to keep track of the vulnerability with a confidential issue.
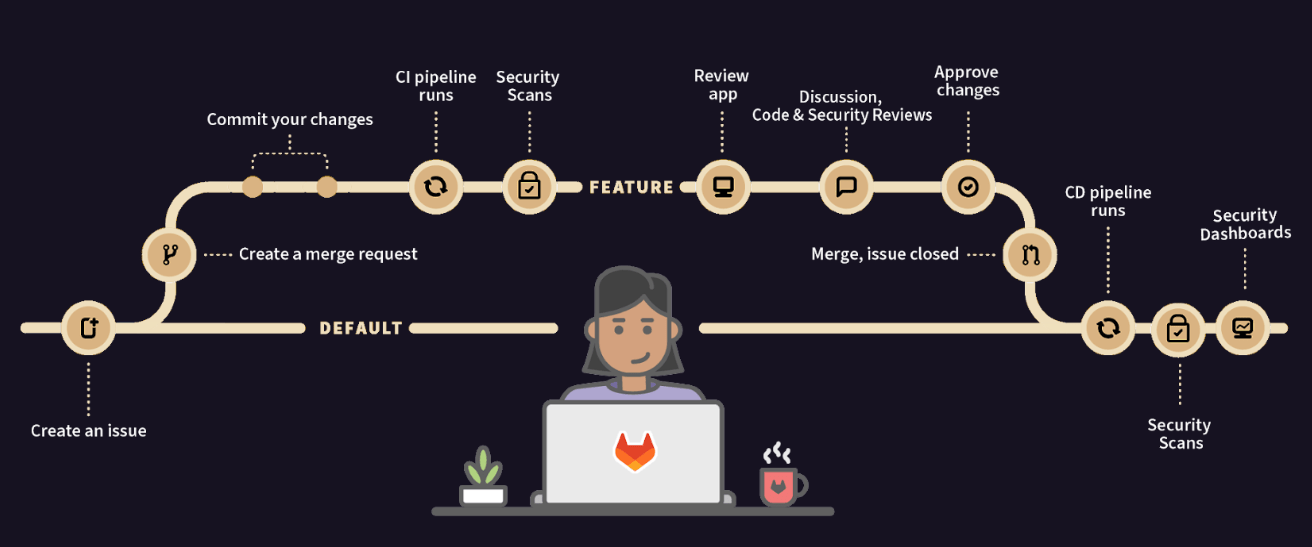
Let's go over how to do the following:
- Implement security scanners in GitLab with built-in templates
- Manage vulnerabilities with the GitLab vulnerability report
- Manage dependencies and generate an SBoM
- Efficiently triage exploitable vulnerabilities with Rezilion
Implement security scanners
The first step in securing your software supply chain is to implement security scanners into your CI/CD pipeline.
These scanners should be set up in a way, where they run on each code commit. When a vulnerability is detected, approval by a security team member should be required.
GitLab offers many different security scanners to get you started:
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Scanning
- Container Scanning
- Dependency Scanning
- Coverage-Guided Fuzzing
- Web-API Fuzzing
- Secret Detection
With the scanners running in a pipeline, static application source code is scanned, as well as dependencies and the
running application itself.
These scanners can be implemented by simply adding templates to your GitLab CI YAML. You can also use the Configuration UI
to set up and configure these security scanners. You can check out the set up instructions for each scanner in the GitLab appsec configuration documentation.
Manage vulnerabilities
Next up, see how to use GitLab to manage vulnerabilities. GitLab provides a single source of truth that allows developers and
appsec engineers to collaborate and address issues together. After the security scanners have been implemented, there are a
few ways to manage vulnerabilities.
Developers will use the MR view to see all the vulnerabilities present in the diff between the feature branch and the branch you are merging with.
You can see below, that each vulnerability is presented in an easy-to-read view:
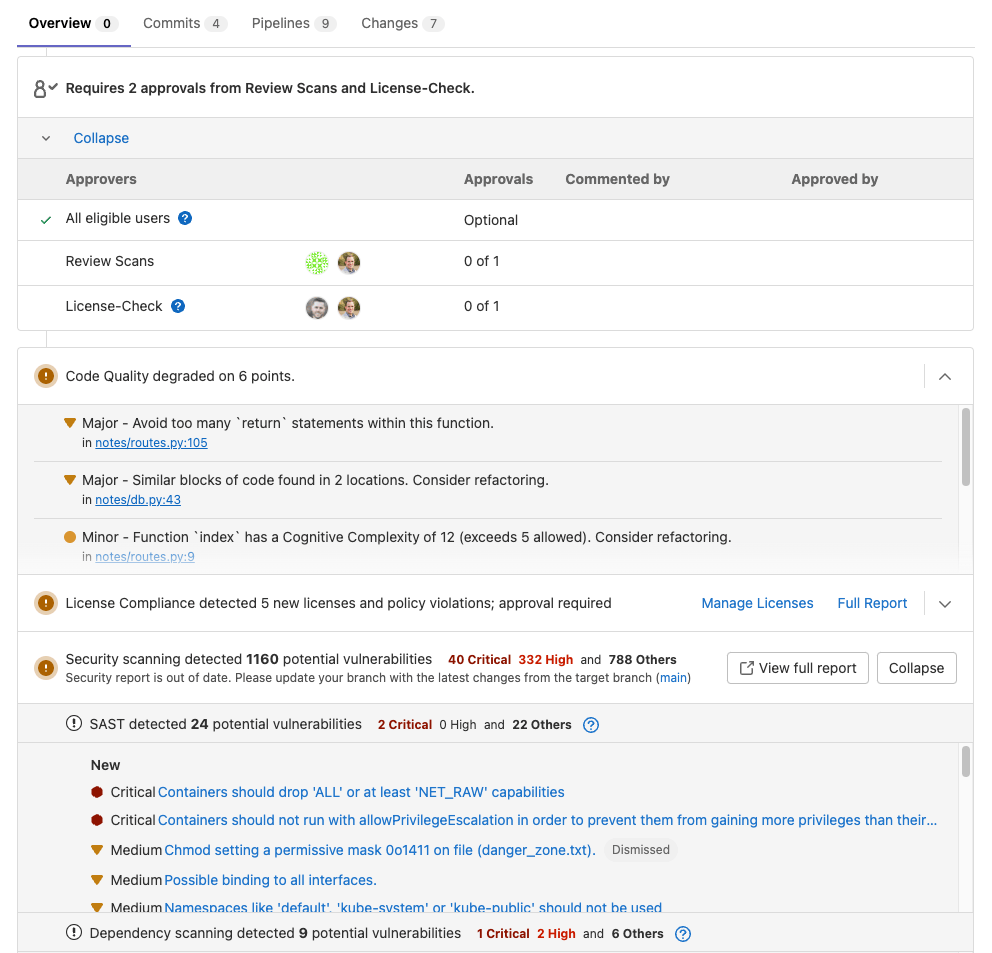
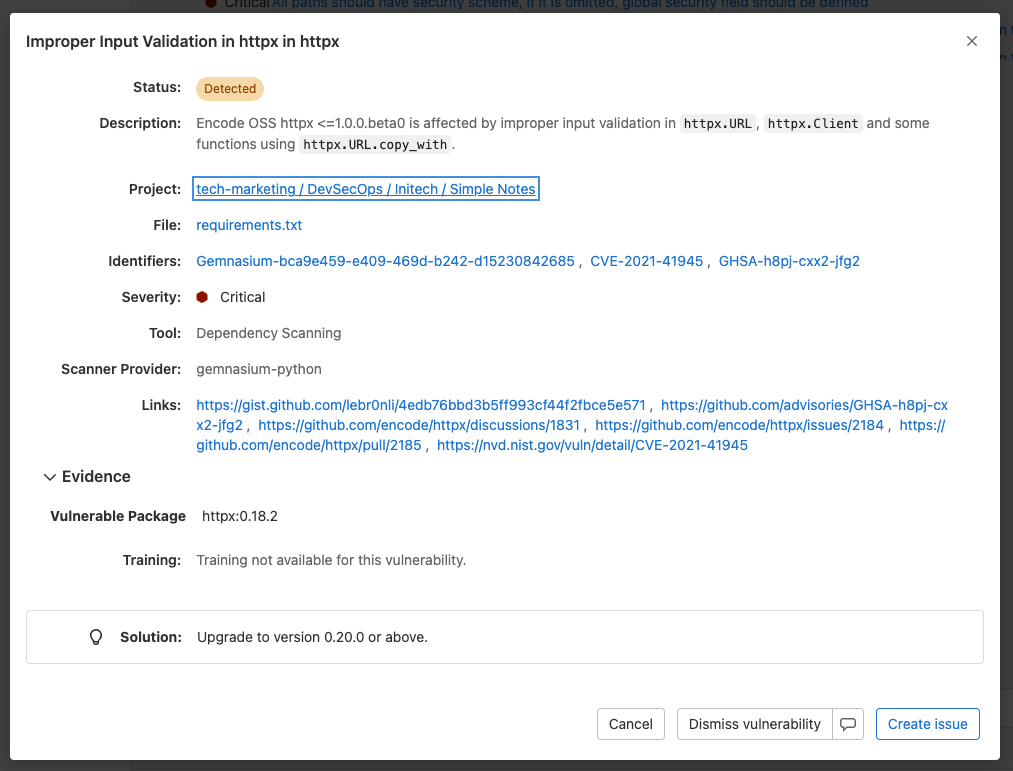
When you click on a vulnerability, you can see details such as:
- Status
- Description
- Evidence
- Severity
- Identifiers
- Linked Issues
- Solution
- Security Training
The vulnerabilities are also actionable which means they can be dismissed or a confidential issue can be created to triage later.
Then there is the vulnerability report which displays all the vulnerabilities detected within the main branch and allows for the
security team to triage and address vulnerabilities from a common interface, enabling collaboration.
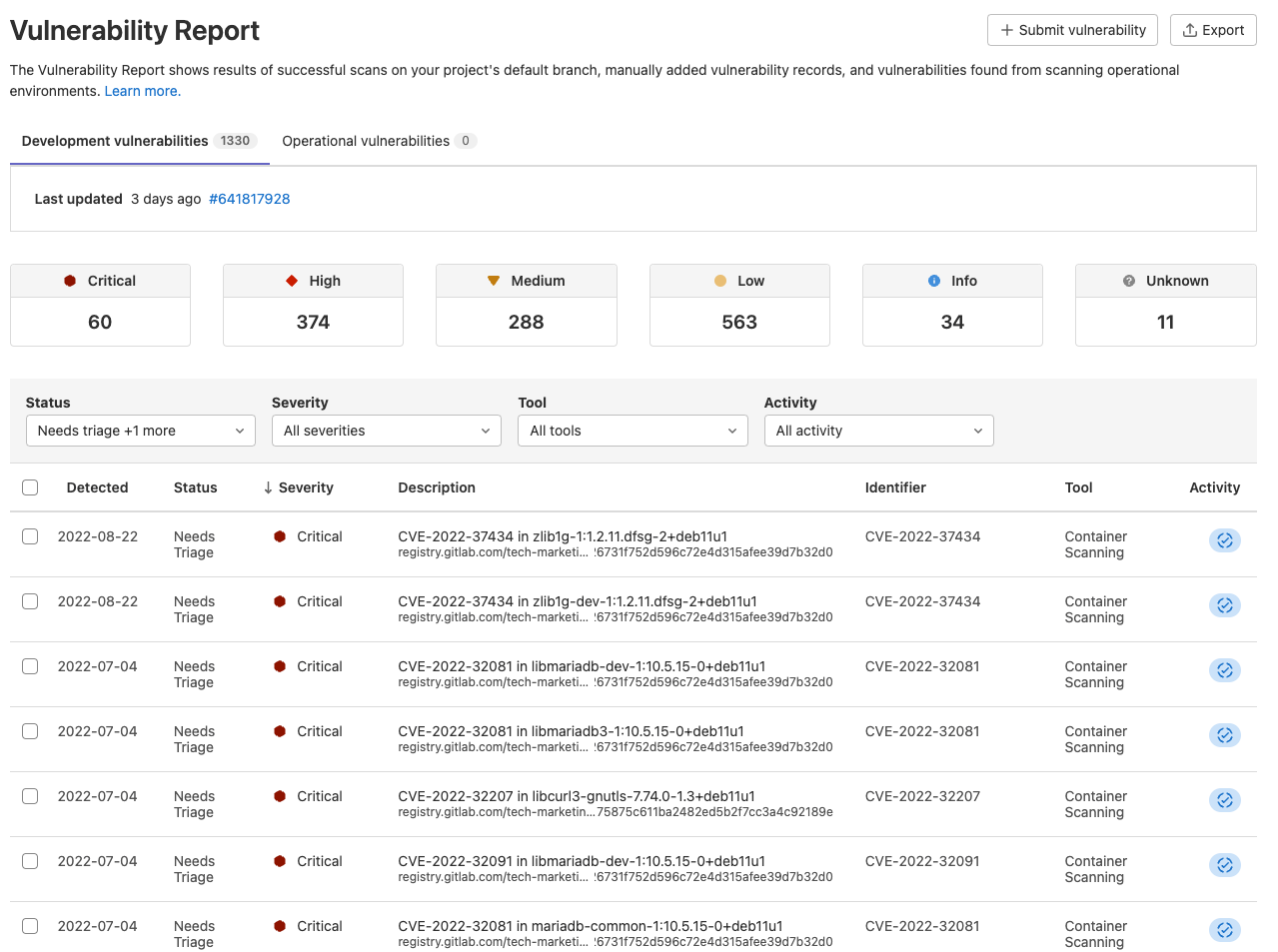
Once you click on a vulnerability, you are provided with advanced details on the vulnerability as well as how to remediate it.
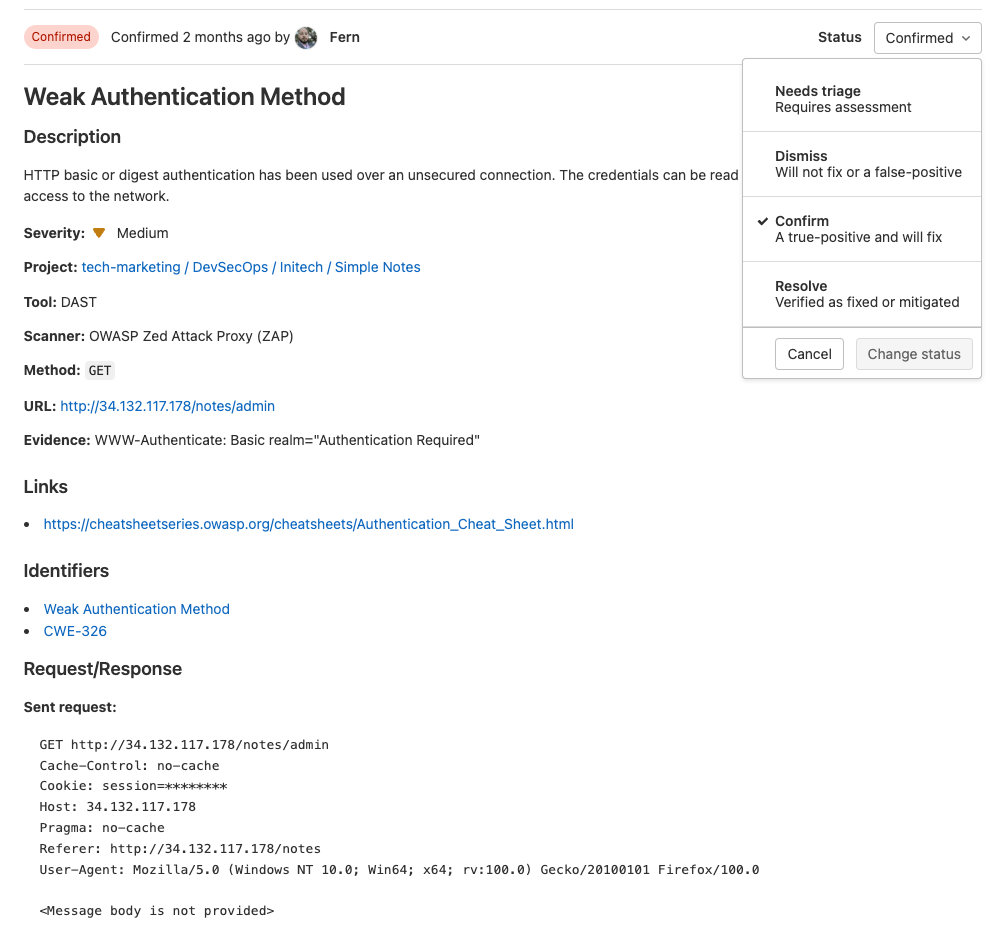
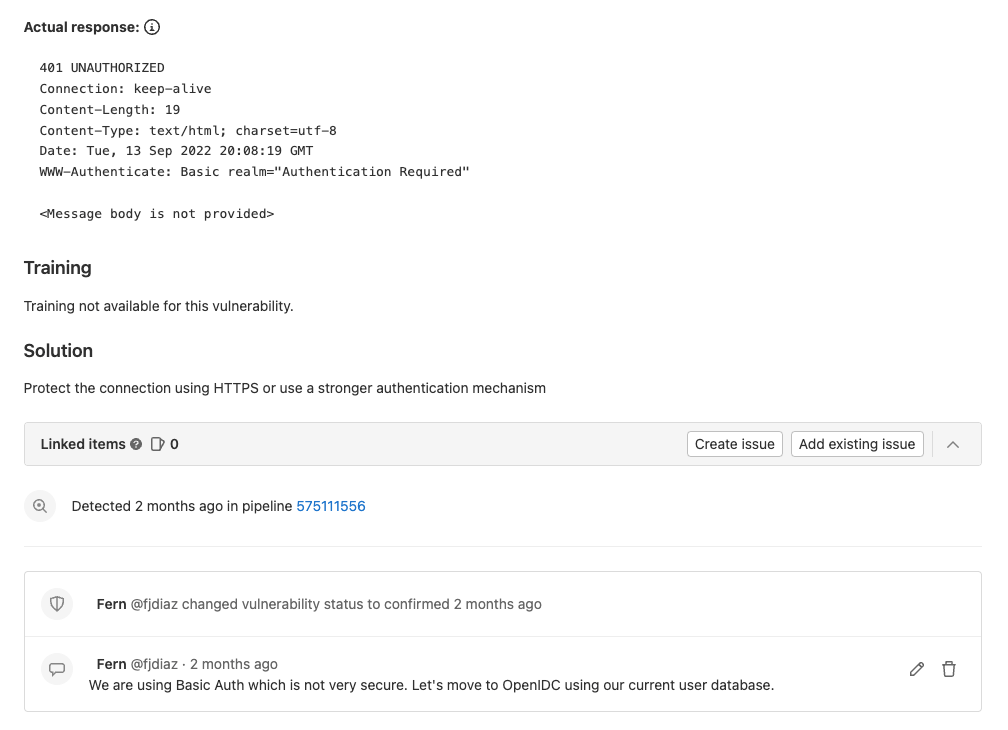
An appsec engineer can change the status, add additional information, and create confidential issues from this view.
Manage dependencies
Now that you have seen how to run security scans on your application, as well as manage vulnerabilities, let's explore managing our
application's dependencies and understanding what is running on your system.
There are a few ways of managing dependencies and generating an SBoM. I'll go over
the GitLab Dependency List (SBoM) as well as the dynamic Rezilion SBoM.
GitLab Dependency List (SBoM)
GitLab provides a Dependency List also known as an SBoM.
The dependency list contains your project’s dependencies and critical details about those dependencies, including their known vulnerabilities. GitLab displays dependencies with the following information:
| Field | Description |
|---|


